源于:论文 范文www.udooo.com
摘 要: 传统的微处理器由于内部有限的逻辑资源和外部固定的引脚封装,大大限制了应用范围。为此,在阐述微控制器的内部结构、存储器管理结构和指令集结构后,利用现场可编程门阵列丰富的逻辑资源,虚拟出传统微控制器的处理器核心,添加Wishbone总线,将处理器核心与通用外设连接构成一个虚拟的微控制器平台,并使用硬件描述语言Verilog和VHDL,自底向上设计R处理器核心,与通用外设互连组成系统,使用XILINX Virtex?Ⅱ Pro芯片进行板级验证。结果表明,实现了既定目标,与标准的微控制器兼容,系统运行稳定。该方法延续了传统微控制器的生命力,能使其得到更大发展。关键词: 微控制器; 哈佛结构; 现场可编程门阵列; Wishbone总线
1004?373X(2013)14?0127?04
Simulation and design of R processor based on VLSI platform
ZHANG Yi?nan1, HE Jing1, YUAN Jie2
(1. Information Science and Engineering Academy of Jinling College, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210089, China;
2. School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China)
Abstract: Internal limited logic resources and external fixed?pin package of traditional microprocessors greatly limit their application range. The internal structure, memory management structure and instruction set architecture of micro control unit (MCU) are described. The abundant logic resources of field programmable gate array (FPGA) are used to virtualize the processor core of traditional MCU. Wishbone bus is added to connect processor core with common peripherals to form a virtual MCU platform. Moreover, the bottom?up design of R core is performed with hardware description languages such as Verilog and VHDL, which is connected with common peripherals to build a system. Board level validation was carried out with XILINX Virtex?II Pro chip. The result shows that the set objective is achieved and the system which runs stable is compatible with standard MCU. This method continues the vitality of traditional MCU, and makes it further progressed.
Keywords: microcontroller; Harvard architecture; field programmable gate array; Wishbone bus
0 引 言
随着社会发展,工业控制及人们日常生活越来越追求精密控制,为满足这种需求,微控制器得到了快速发展。微控制器(Micro Control Unit,MCU)又称单片微型控制计算机或单片机。随着大规模集成电路(Large Scale Integration,LSI)发展,MCU将原本分散的处理器(Central Processor Unit,CPU)、随机存储器(Random Access Memory,RAM)、只读存储器(Read Only Memory,ROM)、输入/输出接口(In/Out Ports,I/O)等集中于一块单晶芯片内,形成一种芯片级计算系统。MCU主要用于控制,MCU构成的系统有实时、快速的外部响应,能迅速采集到大量数据,做出逻辑判断与推理后实现对被控制对象的参数调整与控制。但是随着对控制的要求增大,传统MCU也越来越显得捉襟见肘。为此使用专用应用集成电路(Application Speci?c Integrated Circuit,ASIC)器件在片内实现与传统MCU相兼容的核心,选用合适的片内总线来连接外设,构成一个兼容传统MCU平台,这种方法必会延续传统MCU的生命力,使其获得更大的发展[1?3]。
1 MCU简介
若将4位单片机的出现作为MCU的起点,MCU的发展大致可以分为如下阶段:初级阶段(1971年—1976年)、8位低性能阶段(1976年—1980年)、8位高性能阶段(1980年—1983年)、16位阶段(1983年至80年代末)、片上系统(System On?Chip,SoC)阶段(1990-)。一个通用的MCU由ROM、RAM、GPIO、串行设备(UART/SPI/IIC)、计数器/定时器(TIMER)等组成,并通过总线连接,如图1所示。源于:论文的写法www.udooo.com
摘自:学生论文www.udooo.com

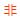 本站原创
本站原创